缓存策略
缓存策略决定了如何处理缓存数据和网络请求之间的关系。@keq-request/cache 提供了多种内置策略,并支持自定义策略。
Strategies.NETWORK_ONLY

仅网络 - 直接发送请求,不使用缓存,等价于不启用缓存中间件。
Strategies.NETWORK_FIRST

网络优先 - 优先尝试发送网络请求,如果失败则返回缓存。
Strategies.CACHE_FIRST
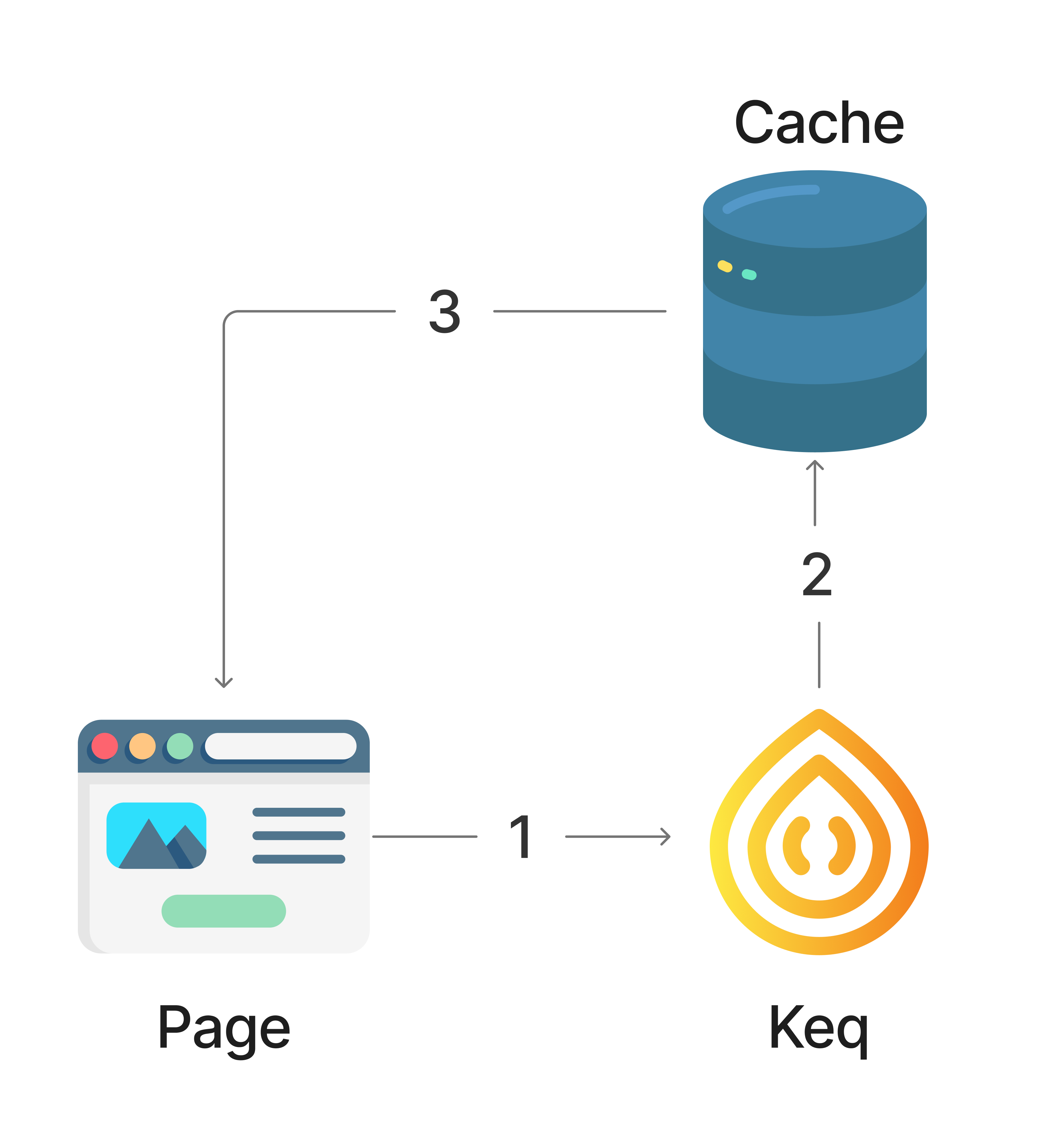
缓存优先 - 如果缓存存在则直接返回,否则发送网络请求。
Strategies.STALE_WHILE_REVALIDATE
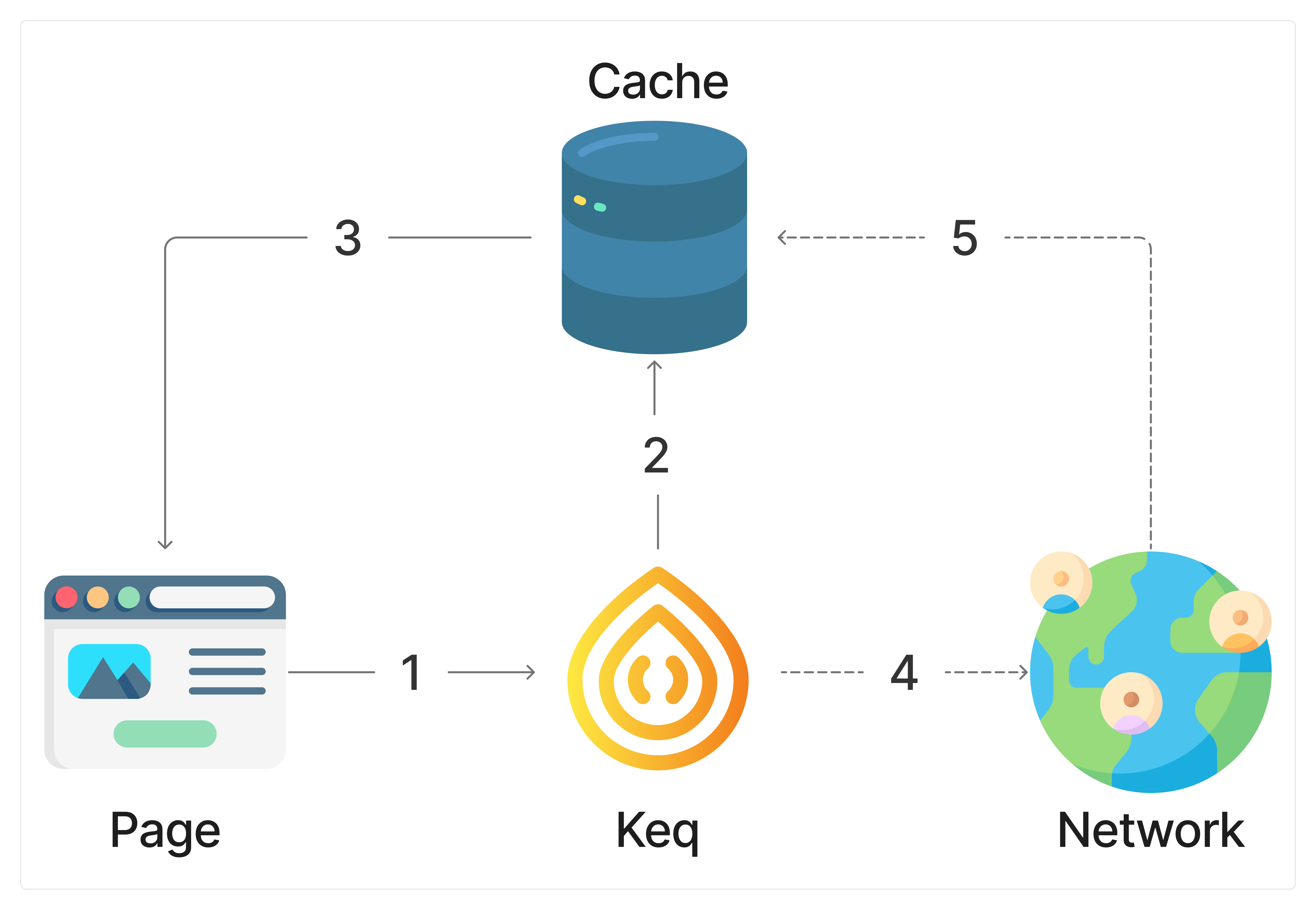
SWR - 如果缓存存在则立即返回缓存,同时异步发送网络请求更新缓存。
自定义策略
你可以实现自己的 Strategy 函数来控制缓存行为。
示例展示了CACHE_FIRST策略的简单实现:
import { request, KeqMiddleware } from "keq"
import { KeqCacheStrategy, KeqCacheParameters, CacheEntry } from "@keq-request/cache"
const MyCacheFirstStrategy: KeqCacheStrategy = async function (handler, context, next) {
// const { storage, key } = params
// return async function (context, next) {
const [key,cache] = await handler.getCache(context)
if (cache) {
context.res = cache.response
context.emitter.emit('cache:hit', { key, response: context.response, context }) // 不要忘记触发缓存命中事件
return
}
context.emitter.emit('cache:miss', { key, context }) // 不要忘记触发缓存未命中事件
// 发送请求
await next()
const [, entry] = await handler.setCache(context, key)
if (entry) {
// 不要忘记触发缓存更新事件
context.emitter.emit('cache:update', {
key: entry.key,
oldResponse: cache?.response,
newResponse: entry.response,
context,
})
}
}
// 接下来你可以直接使用这个自定义策略
request
.get("/example")
.options({
cache: {
key: "custom-cache-key",
strategy: MyCacheFirstStrategy,
ttl: 60,
},
})组合策略
实现全新的策略有些复杂,你需要的可能只是在不同场景下组合内置的策略:
import { KeqCacheStrategy, Strategies } from "@keq-request/cache"
const isNetworkFast = true
const MyStrategy: KeqCacheStrategy = async function (handler, context, next) {
// 根据条件选择不同的策略
if (isNetworkFast) {
return Strategies.NETWORK_FIRST(handler, context, next)
} else {
// 其他情况使用边用边更新
return Strategies.STALE_WHILE_REVALIDATE(handler, context, next)
}
}